codesnippets:firsthaskellprogram
Table of Contents
First Haskell programs
- main function with output, as a complete code example
- compiles, error and warning free, with compiler: GHC 8.10.4, using compiler option -Wall
- executes with the following output:
'x'
- concise explanation of the code
- function
mainis always the entry point of a Haskell program- this is the function that demands the evaluation of the function right to the equal sign (
=)
- function
mainequals to functionprintwith'x'as the first parameter - NOTE: The function
printis a function that will only be evaluated when its evaluation is demanded. Hence, the functionprintnot a command.
- concise explanation of the code elements
- first line declares that function
mainhas typeIO () - second line declares that function
mainequals toprint 'x'- whereas
print, is a function that is imported from a default package - and 'x' is the character
x
- default package is
Prelude - in the second line
main,print, and'x'are functionsmainhas no parameter but has typeIO ()printhas one parameter and has typeShow a ⇒ a → IO ()'x' has no parameter, and has typeChar
IOis a parametric type declared asdata IO a- whereas a is a type parameter, that can be any type
()is the unit type- hence
IO ()is the data typeIOwith type parameter()
Explanation, step by step
first line declares that function ''main'' has type ''IO ()''
IO ()is just a type signature with the resulting typeIO (), and no parameters- see the following code as examples for different type signatures:
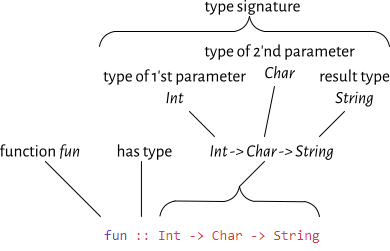
- symbol
→separates parameter from other parameter, and separates from the result type that is on the right hand side - the example shows the follwing 4 type signatures
IO ()- result type:
IO (), no parameter
String → IO ()- result type:
IO (), type of parameter:String
String- result type:
String
Int → Char → String- result type:
String, type of first parameter:Int, type of second parameter:String
- NOTE:
- Types start always with upper case letters.
- Type signatures can also have type parameters, and type constraints.
- Type type parameters start always with lower case letters.
- the example executes with the following output:
"aaaaa"
second line declares that function ''main'' equals to ''print 'x'''
- expression
main = print 'x'is called a binding- it binds
print 'x'to functionmain - when function
mainevaluates it evaluatesprintwith parameter'x'
- expression
sResult = fun 5 'a'is just another binding- it binds
fun 5 'a'to functionsResult - when function
sResultevaluates it evaluatesfunwith parameter5and'a'
default package is Prelude
- package
Preludeincludes standard modules (e.g. module System.IO) - enables basic elements like functions, types, type classes, and instances
- the import of such elements can be controlled in different ways
- see also Avoiding name conflict with Prelude
✎
You could leave a comment if you were logged in.
codesnippets/firsthaskellprogram.txt · Last modified: by 127.0.0.1

